How to Change Watch Battery: Step By Step Guide
Hey Watch Lovers! Keeping your wristwatch running smoothly is essential for ensuring you are always on time and in style. However, even the most reliable timepieces require occasional maintenance, and one of the most common tasks is changing the watch battery. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through the step-by-step process of replacing a watch battery, from recognizing the indications of a low or dead battery to understanding the different types of watch batteries available.
We will also dig into the various types of watch movements, exploring both battery-powered and non-battery-powered options, to give you a complete understanding of how your timepiece operates. Whether you’re a seasoned watch enthusiast or a novice looking to extend the life of your favorite accessory, this guide will equip you with the essential knowledge and skills.
Indications of Watch Battery is Dead or Low
The below are some indications that your watch battery might be dead or low,
- Stopped or Sluggish Movement: If your watch has stopped ticking or is running significantly slower than usual, it could be a sign that the battery is depleted.
- Inconsistent Timekeeping: If you notice that your watch is consistently losing time or stopping altogether, it may be due to a low battery.
- Dim or Flickering Display (for digital watches): Digital watches may show signs of a low battery by having a dim or flickering display.
- Second Hand Skipping: For analog watches, if the second hand begins to skip or moves erratically, it could be a sign of a low battery.
- Digital Functions Not Working: If your watch has additional features like a backlight or alarms and they aren’t functioning properly or at all, it could be due to a low battery.
- Regular Maintenance Reminder: Some watches come with a maintenance reminder, which may indicate that it’s time to replace the battery.
If you notice any of these signs, it’s a good idea to have the battery replaced to ensure the continued functionality of your watch.
Easy Guide to Replace Wrist Watch Battery
Tools Needed
- Watch case opener tool or knife
- Tweezers
- New watch battery (make sure it’s the correct size and type for your watch)
- Soft cloth or mat to protect the watch face
Step-By-Step Guide
Step 01 – Prepare your workspace
Find a clean, well-lit area to work on your watch. Lay down a soft cloth or mat to protect the watch face from scratches.

Step 02 – Remove the watch back
Use a watch case opener tool or a small knife to carefully pry open the back of the watch. Be gentle to avoid damaging the case or injuring yourself. Some watches may have screws holding the back in place, in which case you’ll need a small screwdriver to remove them.
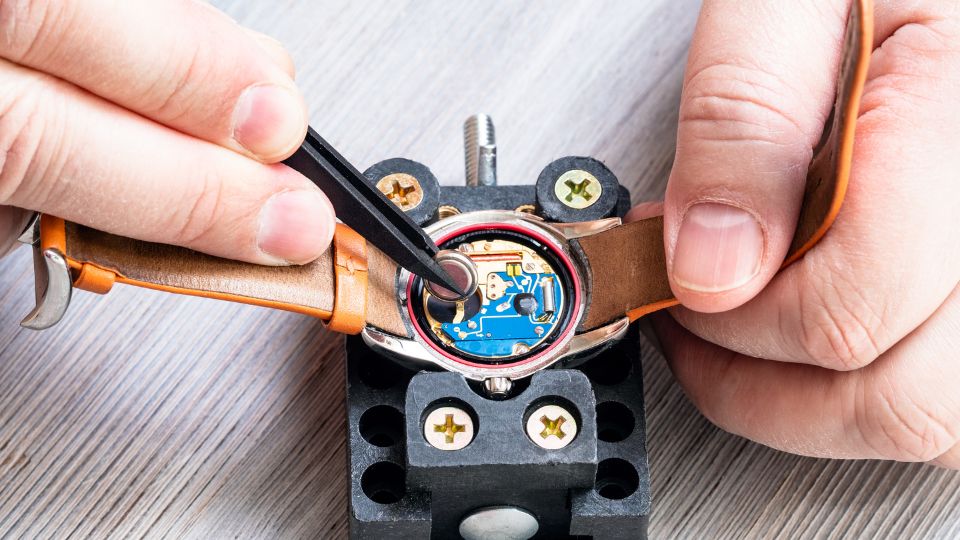
Step 03 – Locate the battery
Once the back is removed, locate the battery inside the watch. It’s usually a round, silver-colored disk.
Step 04 – Remove the old battery
Use tweezers to carefully lift the old battery out of its compartment. Be sure to note which side of the battery is facing up so you can insert the new battery correctly.
Step 05 – Insert the new battery
Take the new battery and place it in the same orientation as the old one, with the correct side facing up. Use the tweezers to press it down gently into the compartment, making sure it’s secure.
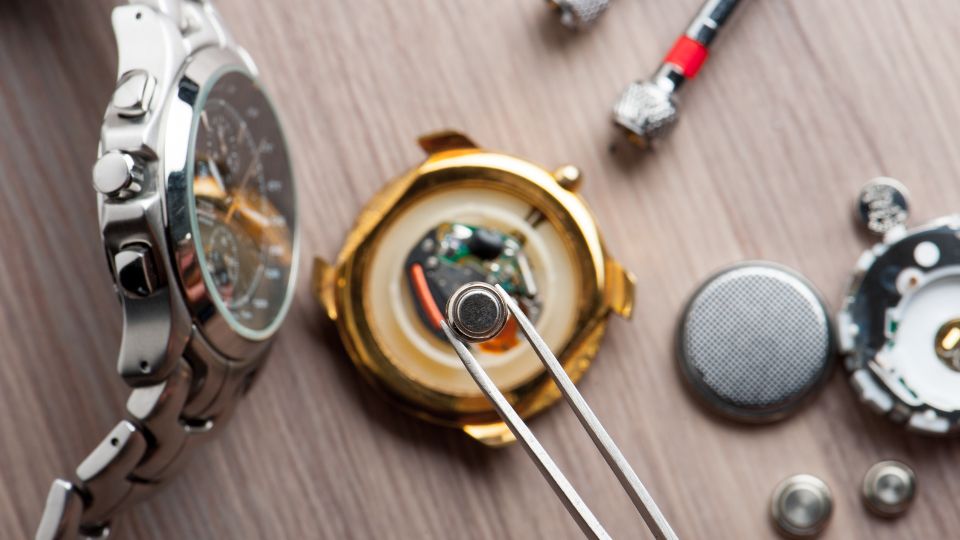

Step 06 – Replace the watch back
Once the new battery is in place, carefully put the back of the watch back on. Make sure it’s aligned properly and press down firmly to snap it into place. If there were screws holding the back in place, reinsert and tighten them securely.
Step 07 – Test the watch
With the back securely in place, test the watch to make sure it’s working properly. Set the time and check that any additional functions are functioning correctly.
Step 08 – Clean the watch
Use a soft cloth to clean any fingerprints or smudges off the watch case.
And that’s it! Your watch should now have a new battery and be ready to wear. If you’re uncomfortable doing this yourself, or if your watch has special features that require professional attention, it is recommended to take it to a jeweler or watch repair shop for battery replacement.
Types of Wrist Watch Batteries
Wristwatches typically use different types of batteries depending on their make, model, and features. Here are some common types of wristwatch batteries,
- Silver Oxide (SR): Silver oxide batteries are the most common type used in wristwatches. They provide a stable voltage and have a relatively long lifespan. These batteries are commonly found in analog watches and watches with basic digital displays.
- Lithium (CR): Lithium batteries are also popular in wristwatches, especially in those with digital displays and advanced features like backlighting and multiple functions. They are known for their high energy density and long shelf life.
- Mercury Oxide (MR): While once common, mercury oxide batteries are being phased out due to environmental concerns. They were often used in older watches but have largely been replaced by silver oxide and lithium batteries.
- Alkaline: Alkaline batteries are less common in wristwatches but may be used in some lower-end models or in watches that require higher voltage. They are less frequently used due to their shorter lifespan compared to silver oxide and lithium batteries.
- Zinc-Air: Zinc-air batteries are relatively rare in wristwatches but are sometimes used in specialized models. They utilize oxygen from the air as a reactant, providing a high energy density.
When replacing a watch battery, it’s essential to use the correct type and size specified by the watch manufacturer to ensure proper function and avoid damage to the watch. If you’re unsure about which battery your watch requires, you can often find this information in the watch’s manual or by consulting a professional watchmaker or jeweler.
Understanding Different Types of Watch Movements
Watches utilize different types of movements (also referred to as “calibers”) to keep time. The below provided are some common types of watch movements and whether they require batteries or not.
- Mechanical Movement: Mechanical movements are powered by a mainspring, which is wound either manually (manual movement) or automatically through the motion of the wearer’s wrist (automatic movement). These movements do not require batteries and instead rely on mechanical components such as gears, springs, and escapements to regulate time.
- Quartz Movement: Quartz movements are powered by a battery and use the vibrations of a quartz crystal to regulate time. When an electric current is applied to the crystal, it vibrates at a precise frequency, which is then converted into timekeeping pulses. Quartz movements are highly accurate and require minimal maintenance.
- Kinetic Movement: Kinetic movements combine the principles of automatic and quartz movements. They feature a rotor that spins with the motion of the wearer’s wrist, similar to an automatic movement, but instead of winding a mainspring, it generates electricity to charge a capacitor or battery, powering a quartz movement. Kinetic movements are self-charging and do not require battery replacements as frequently as traditional quartz movements.
- Solar Movement: Solar movements are powered by a rechargeable battery that is charged by solar cells on the watch face. They convert light into electricity to power a quartz movement. Solar-powered watches are environmentally friendly and require minimal maintenance, as they can be recharged by exposure to both natural and artificial light.
- Mechanical Hand-Wound Movement: This is a type of mechanical movement that requires manual winding via the crown to keep the watch running. It does not use a battery and relies solely on the energy stored in the mainspring.
- Spring Drive Movement: Spring Drive movements are a hybrid of mechanical and electronic technology. They use a mainspring for power but regulate time using an electronic oscillator and electromagnetic braking system. Spring Drive movements do not require batteries but are powered by the energy stored in the mainspring.
In summary, mechanical movements do not require batteries, while quartz, kinetic, and solar movements rely on batteries or capacitors for power. Each type of movement offers unique advantages and characteristics, catering to different preferences and needs among watch enthusiasts.
Types of Wrist Watches Powered by Batteries
Wristwatches powered by batteries are commonly found and come in various types, catering to different preferences and needs. Here are some popular types:
- Analog Watches: Analog watches display time using hour and minute hands along with markers or numerals on a dial. Many analog watches are powered by batteries, particularly those with quartz movements.
- Digital Watches: Digital watches use electronic displays to show the time in numeric form. They often include additional features like alarms, timers, and backlighting. Most digital watches are battery-powered, typically using lithium or silver oxide batteries.
- Smartwatches: Smartwatches are digital watches with additional functionality, such as fitness tracking, notifications, and app integration. They are usually powered by rechargeable batteries, commonly lithium-ion, which can be charged via USB or wireless charging.
- Chronograph Watches: Chronograph watches feature additional stopwatch functions. They can measure elapsed time using one or more subdials and push buttons on the side of the case. Chronograph watches can be either analog or digital and are often battery-powered.
- Dress Watches: Dress watches are typically minimalist in design and are intended for formal or dressy occasions. They can be analog or digital and are commonly powered by batteries, ensuring reliable timekeeping without the need for manual winding.
- Fashion Watches: Fashion watches prioritize style and trends over technical features. They come in various designs and are often battery-powered for affordability and convenience.
- Diving Watches: Diving watches are designed for underwater use and typically feature water resistance, luminous markers, and rotating bezels for measuring dive time. Many diving watches are quartz-powered for accuracy and reliability.
- Aviator Watches: Aviator watches are designed for pilots and often feature additional functions like a slide rule or GMT hand for tracking multiple time zones. They can be analog or digital and are commonly battery-powered.
- Sports Watches: Sports watches are rugged and durable, designed for outdoor activities like hiking, running, or cycling. They often include features like stopwatch functions, GPS tracking, and water resistance. Many sports watches are battery-powered for convenience.
These are just a few examples of wristwatches powered by batteries. Each type offers unique features and characteristics to suit different lifestyles and preferences.
Types of Wrist Watches Which Does Not Need Batteries
Wristwatches can be powered by various means other than batteries. Here are some types of wristwatches that are powered by alternative mechanisms:
- Mechanical Watches: These watches are powered by a mainspring, which is wound manually (manual mechanical) or automatically (automatic mechanical) through the movement of the wearer’s wrist. Mechanical watches use a series of gears, springs, and other mechanical components to keep time.
- Automatic Watches: Automatic watches are a type of mechanical watch that features a rotor, which rotates with the movement of the wearer’s wrist, winding the mainspring. This eliminates the need for manual winding, although occasional manual winding may be necessary if the watch is not worn regularly.
- Kinetic Watches: Kinetic watches combine the traditional mechanical movement with a self-winding mechanism powered by the movement of the wearer’s wrist. They also feature a rechargeable battery that stores the energy generated by the movement, allowing the watch to continue running even when not worn for extended periods.
- Solar-Powered Watches: These watches feature a solar cell on the watch face that converts light into electrical energy to power the watch. The energy is stored in a rechargeable battery, allowing the watch to operate even in low-light conditions. Solar-powered watches are often equipped with power-saving features to extend battery life.
- Radio-Controlled Watches: Radio-controlled watches receive time signals from atomic clocks via radio waves, ensuring extremely accurate timekeeping. These watches typically feature a quartz movement powered by a battery, with the radio receiver adjusting the time automatically based on the received signal.
- Spring Drive Watches: Spring Drive watches, developed by Seiko, combine mechanical and electronic components. They use a mainspring for power but employ an electronic regulator instead of a traditional escapement to control the release of energy from the mainspring. This results in highly accurate timekeeping and a smooth sweeping second hand.
These are just a few examples of wristwatches powered by mechanisms other than batteries. Each type offers unique advantages and characteristics, catering to different preferences and needs among watch enthusiasts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1 – How often should I replace my wristwatch battery?
The lifespan of a watch battery varies depending on factors such as the type of watch, the quality of the battery, and how frequently the watch is used. On average, a watch battery may last anywhere from one to five years. If you notice signs of a low battery, such as the watch running slow or stopping, it’s time for a replacement.
Q2 – Can I replace the battery myself or should I go to a professional?
Whether you can replace the battery yourself depends on your comfort level with watch maintenance and the type of watch you have. Some watches have easy-to-access battery compartments, while others require specialized tools and skills to open. If you’re unsure or uncomfortable, it’s best to take your watch to a professional jeweler or watchmaker for battery replacement.
Q3 – How do I know which battery my watch needs?
The type and size of the battery your watch requires are usually indicated in the watch’s manual or on the back of the watch case. You can also look up this information online using the watch’s model number. If you’re still unsure, a professional jeweler or watchmaker can help you identify the correct battery.
Q4 – What should I do if I can’t find the right battery for my watch?
If you’re having trouble finding the correct battery for your watch, consider taking it to a professional jeweler or watch repair shop. They often have a wide selection of watch batteries and the expertise to identify the right one for your watch.
Q5 – How do I prevent damaging my watch while replacing the battery?
To prevent damaging your watch during battery replacement, use the proper tools and techniques. Be gentle when opening the watch case and handling the delicate internal components. Avoid touching the movement or other sensitive parts with your fingers, as oils from your skin can cause damage.
Q6 – Can I reuse the old watch battery?
It’s not recommended to reuse old watch batteries, as they may be depleted or damaged. Always use a new, high-quality battery when replacing the battery in your watch to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Q7 – What should I do with the old battery?
Dispose of old watch batteries properly according to local regulations. Many communities have recycling programs for household batteries, including watch batteries. You can also take the old battery to a recycling center or return it to the retailer where you purchased the new battery.





